Beware, ‘wannaCry’ malware spreading very rapidly and hitting businesses across the world. Know more about this malware.

A malicious software called ‘ransomware’ has forced British hospitals to turn away patients and affected Spanish companies such as Telefonica as part of a global outbreak that has affected tens of thousands of computers. Here’s a look at how ransomware works and what people can do if they fall victim to attacks.
What is WannaCry?
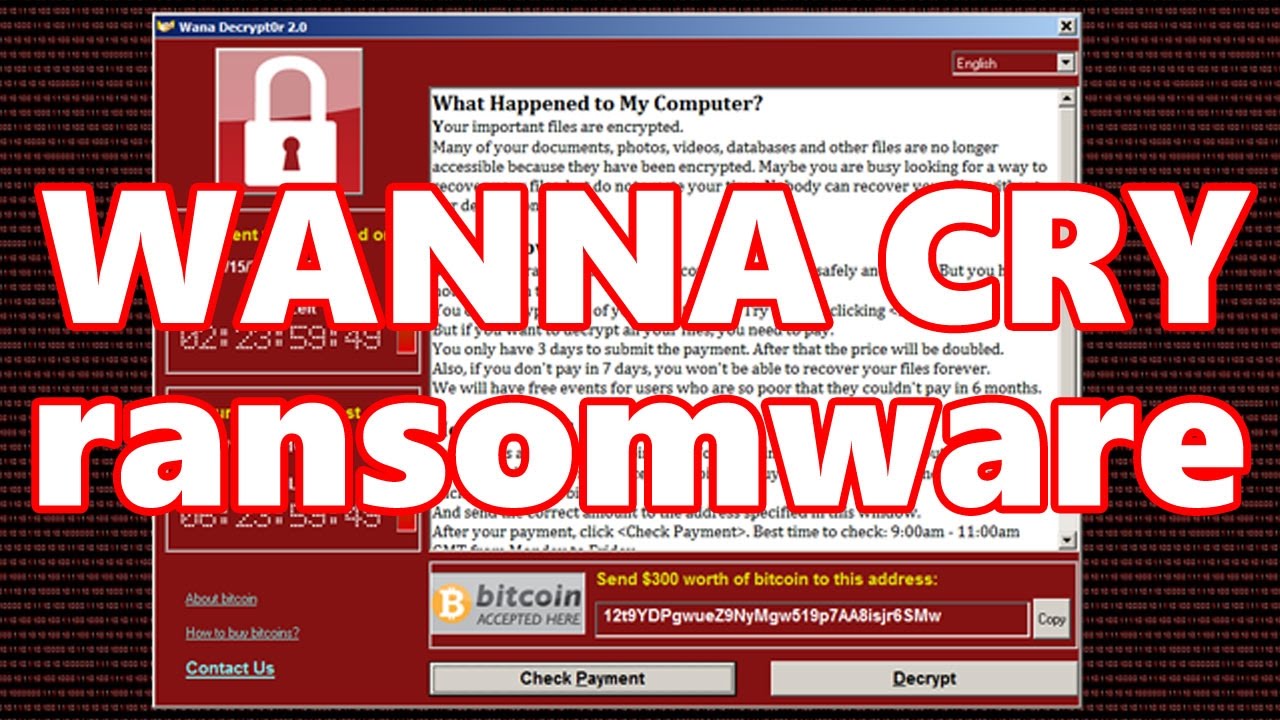
WannaCry, also known as WanaCrypt0r 2.0, WannaCry and WCry, is a form of “ransomware” that locks up the files on your computer and encrypts them in a way that you cannot access them anymore. Ransomware is a program that gets into your computer, either by clicking on the wrong thing or downloading the wrong thing, and then it holds something you need to ransom.
How does it work and spread?
The WannaCry program encrypts your files and demands payment in bitcoin in order to regain access. Security experts warn there is no guarantee that access will be granted after payment. Some ransomware that encrypts files ups the stakes after a few days, demanding more money and threatening to delete files altogether.
There are different variants of what happens: Other forms of ransomware execute programs that can lock your computer entirely, only showing a message to make payment in order to log in again. There are some that create pop-ups that are difficult or impossible to close, rendering the machine difficult or impossible to use.
Where has it spread?
British based cyber researcher Chris Doman of AlienVault said the ransomware looks to be targeting a wide range of countries, with initial evidence of infections in at least two dozen nations according to experts from three security firms. According to the researchers, the broad based ransomware attack has appeared in at least eight Asian nations, a dozen countries in Europe, Turkey and the United Arab Emirates and Argentina and appears to be sweeping around the globe.
What is so special about WannaCry?
WannaCry is not just a ransomware program, it’s also a worm. This means that it gets into your computer and looks for other computers to try and spread itself as far and wide as possible.
Ransomware has a habit of mutating and so it changes over time in order to find different ways to access computers or to get around patches (operating system updates that often include security updates). Many security firms are already aware of WannaCry in past forms and most are looking at this one right now to see how it might be stopped.
Who is behind this cyber attack?
WannaCry exploited a vulnerability in the Windows operating system believed to have been developed by the United States’ National Security Agency (NSA), which became public last month. It was among a large number of hacking tools and other files that a group known as the Shadow Brokers released on the Internet. Shadow Brokers said that they obtained it from a secret NSA server. The identity of Shadow Brokers is unknown though many security experts believe the group that surfaced in 2016 is linked to the Russian government.
What can you do?
Several cyber security firms said WannaCry exploits a vulnerability in Microsoft and that Microsoft patched this in March. People don’t always install updates and patches on their computers and so this means vulnerabilities can remain open a lot longer and make things easier for hackers to get in.
Users should regularly back up their data and ensure that security updates are installed on your computer as soon as they are released. Up-to-date backups make it possible to restore files without paying a ransom.
Users should also look for malicious email messages that often masquerade as emails from companies or people you regularly interact with online. It’s important to avoid clicking on links or opening attachments in those messages, since they could unleash malware.

 Currency Convertor
Currency Convertor Post an article
Post an article eLive Today.
eLive Today.

 sending...
sending...




